DIVISION NEWS
-
Dan MacDonald awarded Banting Fellowship
Daniel MacDonald, a Research Fellow in the Gibson Lab, is a 2024 recipient of the Banting Postdoctoral Fellowship. The Banting Postdoctoral Fellowship program provides funding to the very best postdoctoral […]
-
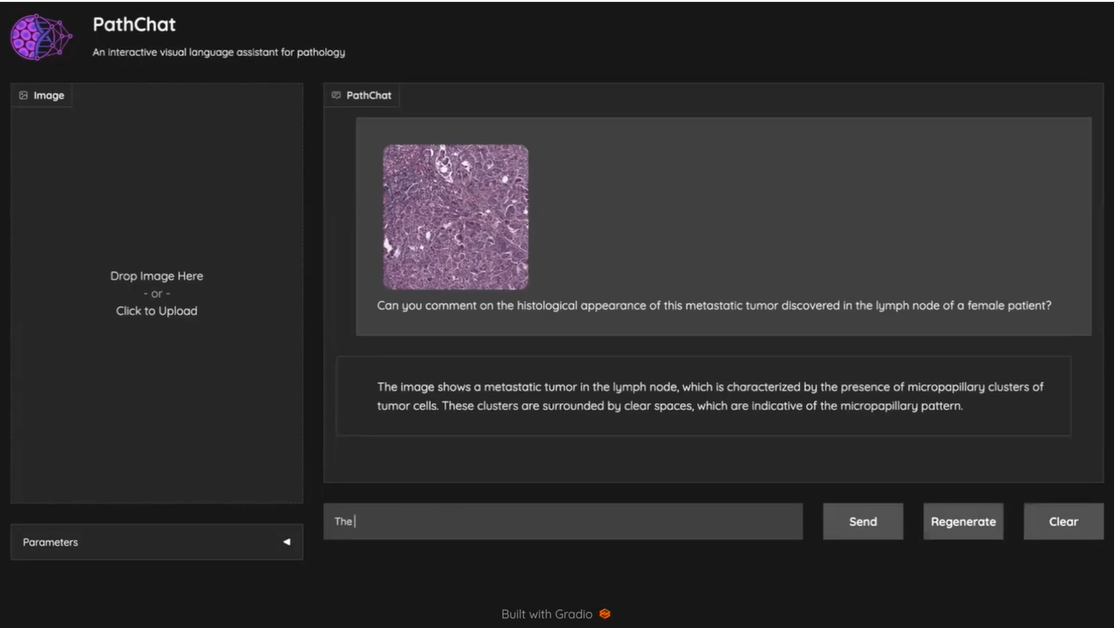
Mahmood Lab releases PathChat, a vision-language AI assistant for Pathology
Developed by the Mahmood Lab, PathChat is a vision-language AI assistant for Pathology that can analyze histology images and answer diverse pathology-related queries. See a demonstration of PathChat. The PathChat publication […]
-
May ABC Seminar: Jean du Terrail, PhD – Owkin – “Federated Learning in Healthcare in the Real-World: Examples and Practical Challenges”
With the never-ending revolutions of data-driven approaches that started already more than a decade ago, it is surprising at first that the pace of ML discoveries in medicine seems substantially slower than the ones found in consumer applications such as ChatGPT. The answer to that paradox is relatively simple: in healthcare, data is hard to…
-
Special Seminar: Anshul Kundaje, PhD – “Using deep learning models to debug regulatory genomics experiments and decode cis-regulatory syntax”
BWH Computational Pathology Special Seminar Title: Using deep learning models to debug regulatory genomics experiments and decode cis-regulatory syntax Speaker: Anshul Kundaje, PhD Affiliation: Stanford University Position: Associate Professor, Genetics […]
-
Nature Medicine Publications detail Mahmood Lab’s Design of AI Foundation Models to Advance Pathology
Two foundation models for pathology AI developed by the Mahmood Lab published in Nature Medicine: UNI and CONCH. Foundation models, advanced artificial intelligence systems trained on large-scale datasets, hold the […]
-
March ABC Seminar: Andrew H. Song – Brigham and Women’s Hospital – “Towards 3D pathology – The opportunities and challenges”
Human tissue, which is inherently three-dimensional (3D), is traditionally examined through standard-of-care histopathology as limited two-dimensional (2D) cross sections that can poorly represent the tissue due to sampling bias. To […]
-
February ABC Seminar: Vitalii Kleshchevnikov, PhD – Wellcome Sanger Institute – “Probabilistic models to resolve cell identity and tissue architecture”
Cell identity drives cell-cell communication and tissue architecture and is in return regulated by cell-extrinsic cues. Cell identity is determined by the combination of intrinsic developmentally established transcription factor use […]
-
December ABC Seminar: Miriam Adler, PhD – Hebrew University
Fibrosis is a pathology of excessive scarring which causes morbidity and mortality worldwide. Fibrosis is a complex process involving thousands of factors, therefore, to better understand fibrosis and develop new […]
-
November ABC Seminar: Gennady Gorin, PhD – CalTech
Stochastic foundations for single-cell RNA sequencing Single-cell RNA sequencing, which quantifies cell transcriptomes, has seen widespread adoption, accompanied by a proliferation of analytic methods. However, there has been relatively little […]